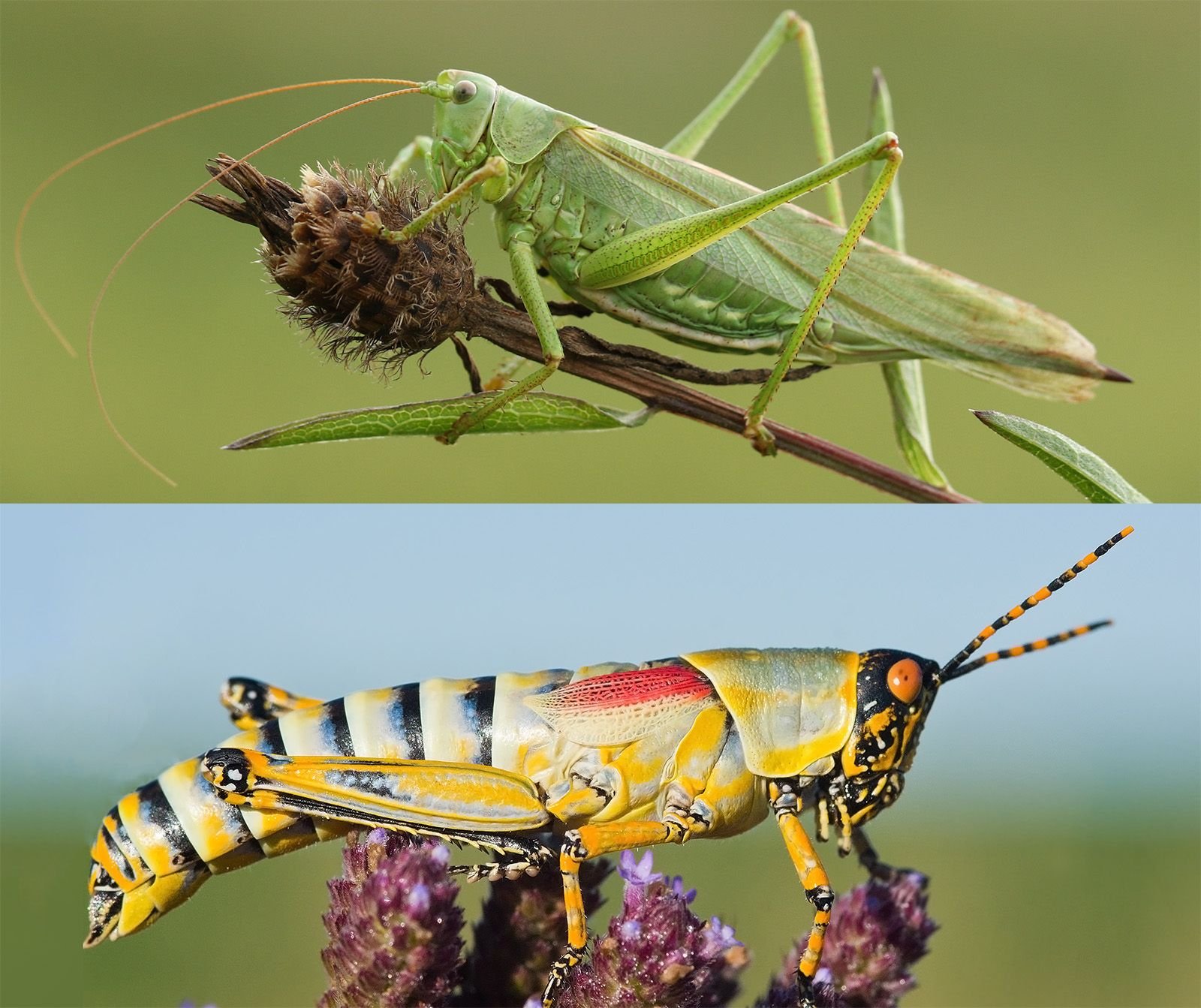
Crickets & grasshoppers are both members of The order Orthoptera. Sharing similarities like long hind legs adapted for jumping & a diet primarily consisting of plants. However. They differ in their physical characteristics & behaviors; crickets typically have a more curved body & produce distinct sounds by rubbing their wings together. While grasshoppers possess a more elongated body & often have a quieter disposition. Additionally. Crickets are nocturnal. While grasshoppers are primarily active during The day. Highlighting their ecological adaptations & lifestyle differences despite their shared lineage.
Cricket vs Grasshopper: Differences and Similarities. Discover The fun differences & similarities between crickets & grasshoppers! Dive into their unique traits & learn what makes these insects special.
What is Cricket vs Grasshopper: Differences & Similarities & how does it work?
Cricket & grasshopper belong To an order called Orthoptera. Both creatures share features. Like long hind legs for jumping. Cricket sings. While grasshopper produces sounds through stridulation. Crickets prefer moist environments; grasshoppers thrive in dry areas. Both insects undergo similar life cycles. Including egg. Nymph, & adult stages.
Brief history of Cricket vs Grasshopper: Differences & Similarities
Originating millions of years ago. Crickets evolved from early Orthoptera. Grasshoppers followed a similar evolutionary process. Crickets gained popularity in many cultures for entertainment & pest control. Grasshoppers contributed significantly To ecosystems as herbivores. Differences in habitats led each species down unique evolutionary paths.
How To implement Cricket vs Grasshopper: Differences & Similarities effectively
Understanding habitats helps in observing both insects. Collect data on their behaviors & interactions. Encourage habitat preservation for both species. Initiate programs that promote awareness concerning their roles in ecosystems. Engage communities in citizen science projects focusing on insect monitoring.
Key benefits of using Cricket vs Grasshopper: Differences & Similarities
Crickets contribute nutrients as decomposers. Their singing can reduce stress in humans. Enhancing well-being. Grasshoppers serve as food sources for many birds & amphibians. Both insects help maintain ecological balance & foster biodiversity. They also inspire scientific research into insect behavior.
Challenges with Cricket vs Grasshopper: Differences & Similarities & potential solutions
Habitat loss poses a significant threat To both species. Insecticides often harm these beneficial insects. Conservation efforts must focus on preserving their natural habitats. Promoting organic farming can reduce pesticide usage. Public education regarding their importance aids in conservation.
Future of Cricket vs Grasshopper: Differences & Similarities
Research into insects continues To grow. Offering new insights. Innovations in agriculture may enhance their roles as control agents. Citizen science will likely increase interest in insect monitoring. Conservation efforts for these creatures become more critical with climate change. Understanding their interactions will help in future ecological studies.
Table of Cricket vs Grasshopper: Differences & Similarities
| Feature | Cricket | Grasshopper |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat | Moist environments | Dry areas |
| Sound Production | Sings | Stridulates |
| Diet | Decomposers | Herbivores |
| Life Cycle | Egg. Nymph. Adult | Egg. Nymph. Adult |

Cricket & Grasshopper: Classification
Crickets belong To family Gryllidae. While grasshoppers belong within Acrididae. Both insects fall under order Orthoptera. Orthoptera varies widely. Showcasing numerous species worldwide. Crickets exhibit distinct body features compared To grasshoppers.
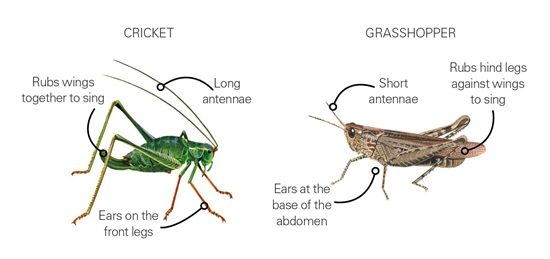
Crickets have long. Thin bodies. While grasshoppers possess stockier appearances. Antennas on crickets tend To be longer. Enhancing their sensory capabilities. Grasshoppers. However. Have shorter antennas. Which affect their perception. Generally. These classifications help entomologists understand similarities & differences.
Physical Characteristics
Crickets showcase slender bodies ranging from 1 To 10 cm long. Characterized by long legs & prominent antennae. Grasshoppers. In contrast. Typically feature thicker bodies. Generally measuring between 2 & 7 cm. These variations impact locomotion capabilities.
Coloration differs significantly between these groups. Crickets mostly exhibit brown or black. Lending them an ability To camouflage. Grasshoppers. However. Display brighter colors. Such as green or yellow. Providing them with visual distinctions. Functional adaptations in coloration arise from their habitats.
Wings also present differences; crickets have longer. More membranous wings. While grasshoppers have shorter wings. This affects their flight patterns & capabilities. Crickets favor quieter environments. Whereas grasshoppers thrive in open spaces.
Habitat Preferences
Crickets prefer dark. Moist environments. Often choosing To inhabit grassy areas or under leaf litter. Their preference for humidity helps them maintain optimal moisture levels. Conversely. Grasshoppers are commonly found in sunny areas. Grasslands, & fields.
Grasshoppers thrive in dry conditions. Requiring less moisture for survival. This difference in preferred habitats is a significant factor influencing their behavioral patterns. Insects exhibit flexibility when adjusting To diverse environments.
Understanding these habitat preferences allows researchers To study ecological roles of both insects. Observations help clarify interactions with other species. Revealing crucial relationships within ecosystems.
Feeding Habits
Crickets are known as omnivores; they consume plant materials. Seeds, & decaying organic matter. They play an important role in nutrient recycling within ecosystems. Their varied diet allows them To adapt based on available food sources.
Grasshoppers primarily act as herbivores. Focusing on grasses & leaves. Their diet tends To be more restrictive. Which limits their adaptability in certain environments. Grasshoppers help control vegetative growth in their habitats.
Food sources significantly affect reproduction & survival rates among both insects. Optimal nutrition supports successful growth & increases reproductive success. Differences in feeding habits contribute greatly To insect population dynamics.
Reproductive Behaviors
Crickets engage in unique courtship rituals. Characterized by sound production. Male crickets produce distinctive calls. Attracting females for mating. Each species displays unique sounds. Facilitating mating compatibility.
Grasshopper mating practices differ; they often rely less on sound & more on visual cues. Males often demonstrate their fitness through body movements. This method helps signal readiness for mating. Allowing females To evaluate prospective mates.
These reproductive strategies reflect evolutionary pressures faced by each species. Successful reproduction ensures future generations continue within their respective environments. Understanding their mating behaviors can aid in species conservation efforts.
Life Cycle Differences
Crickets undergo a type of development known as incomplete metamorphosis. Eggs hatch into nymphs. Which resemble miniature adults. After several molts. Nymphs mature into fullgrown crickets. Life spans vary based on environmental conditions & available resources.
Grasshoppers also display incomplete metamorphosis. Following a similar developmental pattern. Grasshopper nymphs emerge from eggs. Resembling adults, & grow through subsequent molts. Life span ranges among species. Influenced by habitat & diet.
Both insects exhibit resilience in their life cycles. Adaptations help them thrive in various environments. Studying their growth patterns provides valuable insights into species behavior & ecology.
Sound Production
Sound production plays a crucial role for crickets in communication. Males rub their wings together. Creating chirping sounds. This calling serves multiple purposes. Such as attracting mates & defending territories.
Grasshoppers do not rely heavily on sound; instead. They utilize visual displays for communication. These visual signals may involve body movements or coloration changes. These communication methods demonstrate adaptations based on ecological needs.
Differences in sound production reveal varying evolutionary paths taken by these insects. Understanding their communication strategies can provide insight into their social structures & ecological interactions.
Locomotion & Movement
Crickets primarily rely on jumping as a mode of locomotion. Their long hind legs enable powerful jumps useful for escaping predators. They also exhibit crawling behaviors for navigating through dense vegetation.
Grasshoppers share similar jumping capabilities but possess a slightly different movement style. Their stocky bodies allow for more stable landings & agile maneuvers. Consequently. They can navigate quickly through open spaces.
Both insects demonstrate remarkable adaptations for survival. These adaptations enhance their ability To evade predators & find suitable habitats. Analyzing locomotion offers essential insights into their survival strategies.
Predation & Defense Mechanisms
Crickets face numerous predators. Including birds. Reptiles, & small mammals. Their coloration & habitat preferences often play vital roles in evading capture. Camouflage helps them blend into surroundings. Reducing detection risks.
Grasshoppers also encounter similar predation threats. However. Their coloration contrasts more often with environment. Making them potentially easier targets. Grasshoppers compensate through rapid jumps & evasive movements.
Defense mechanisms vary widely between these insects. Efficient predation responses enhance their chances of survival. Understanding these adaptations offers important perspectives on their ecological roles.
Ecological Roles
Both crickets & grasshoppers act as essential components within ecosystems. These insects contribute significantly To food chains. Supporting various predators. Their presence indicates overall ecosystem health & stability.
Crickets especially assist in decomposing organic material. Enhancing soil fertility. They help break down plant material. Recycling nutrients back into The environment. This function promotes biodiversity & supports plant growth.
Grasshoppers influence vegetation dynamics. Their feeding habits can control plant species’ growth. Impacting local biodiversity. Analyzing these ecological roles reveals intricate relationships between species within habitats.
Population Dynamics
Population dynamics for crickets & grasshoppers fluctuate across seasons. Environmental changes. Appropriate food sources, & predation pressure all influence population sizes. Observing these dynamics reveals essential ecological trends.
Crickets tend To emerge after rainy seasons. Coinciding with increased moisture levels. Ample food sources promote rapid population growth. Grasshopper populations may rise following dry periods. Revealing competitive advantages under certain conditions.
Understanding these fluctuations assists researchers in monitoring ecosystem health. Data collected on population trends can help predict ecological shifts. Maintaining biodiversity serves as an important goal for conservationists.
Behavioral Patterns
Crickets exhibit nocturnal behaviors. Preferring nighttime activity. They rely on darkness for feeding & reproductive activities. Nocturnal habits reduce predation risks while allowing optimal resource exploitation.
Grasshoppers are diurnal. Engaging in activities during daytime. Their exposure enhances visibility but increases predation risks. However. Their bright coloration may also serve as a warning signal for potential threats.
These behavioral differences reflect evolutionary adaptations based on ecological niches. Each insect employs strategies that suit its respective environment & lifestyle. Studying these patterns provides valuable insights into species survival.
Interactions with Humans
Crickets hold cultural significance across many societies. They symbolize good luck in some cultures. Often featured in folk tales & stories. Additionally. Some communities utilize crickets in traditional medicine.
Grasshoppers share similar cultural relevance but not as widely recognized. In some cultures. They remain edible. Providing protein sources for communities. This use highlights potential importance To local economies.
Interactions with humans show varying implications for species conservation. Ensuring balanced relationships promotes ecological sustainability. Cultural perceptions influence conservation efforts. Shaping attitudes toward these insects.
Conservation Status
Crickets. In general. Maintain stable populations. But habitat destruction poses risks. Urbanization & agricultural expansion threaten their natural habitats. Conservation efforts must focus on habitat restoration & awareness campaigns.
Grasshoppers face similar threats. Particularly due To landscape changes. Some species face declining populations. Necessitating protective measures. Analyzing conservation statuses helps prioritize efforts for atrisk species.
Awareness of these conservation issues can foster community engagement. Increased public understanding promotes greater support for biodiversity initiatives. Individuals can play an important role in safeguarding these unique insects.
Fun Facts About Crickets & Grasshoppers
- Crickets can live up To 90 days! 🦗
- Grasshoppers can jump up To 20 times their body length! 🦗
- Crickets create songs by rubbing wings together. 🎵
- Grasshoppers have a unique ability called ‘phototaxis.’ 🌞
- Crickets are often used in scientific studies as model organisms. 🔬
- Grasshoppers display various colors based on species. 🎨
| Specification | Cricket | Grasshopper |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Classification | Order: Orthoptera, Family: Gryllidae | Order: Orthoptera, Family: Acrididae |
| Body Structure | Elongated body, long antennae | Stocky body, short antennae |
| Color | Usually brown or black | Often green or brown |
| Sound Production | Produces sound by rubbing wings together (stridulation) | Primarily produces sound by rubbing hind legs against wings |
| Habitat | Prefer moist environments like grasslands and shrubs | Inhabit dry, open areas such as fields and grasslands |
| Diet | Omnivorous (grass, leaves, fruits) | Herbivorous (grasses and leaves) |
| Reproduction | Lay eggs in soil, often in the fall | Lay eggs in soil or vegetation, can lay multiple times a season |
| Life Cycle | Egg, nymph, adult | Egg, nymph, adult |
| Size | Generally 1-2 inches long | Typically 0.5-4 inches long |
| Wings | Two pairs of wings, used for flight | Two pairs of wings, primarily for gliding |
| Behavior | Sings to attract mates, territorial | More solitary, less vocal |
| Locomotion | Fast and agile jumpers | Powerful jumpers, can leap long distances |
| Camouflage | Blend with surroundings, often darker | Can mimic grass and leaves to avoid predators |
| Common Species | House cricket, field cricket | Common field grasshopper, meadow grasshopper |
| Environmental Role | Soil aeration, prey for birds and small mammals | Prey for birds, reptiles, and other predators |
| Communication | Uses chirping as a primary means | Uses drumming sounds and body movements |
| Predators | Birds, mammals, reptiles | Birds, frogs, and larger insects |
| Commercial Use | Used as food for pets, in some cultures as food | Often studied in ecological research |
| Famous Traits | Crickets are often associated with good luck | Grasshoppers are known for their hopping agility |
Cricket vs Grasshopper: Differences & Similarities
Overview of Crickets
Crickets belong within The family Gryllidae. These insects exhibit long antennae & robust bodies. Their songs are created by rubbing their wings together. This sound attracts mates & establishes territory. Many cultures appreciate crickets for their singing. Their diet mainly consists of organic matter. Including decaying leaves.
Crickets reside in various habitats. Primarily grasslands. Forests, & even caves. These environments sustain their growth & reproductive needs. Additionally. Crickets display nocturnal behavior. Becoming active during night hours. This adaptation helps them avoid daytime predators. Their unique behaviors make crickets fascinating within ecological studies.
Crickets play essential roles in ecosystems. They contribute To soil health through decomposition. Moreover. These insects serve as dietary components for animals like birds. Amphibians, & small mammals. Thus. Crickets maintain vital relationships within food webs.
Overview of Grasshoppers
Grasshoppers belong within The Caelifera suborder. These insects showcase thick bodies & short antennae. Their agility allows them To jump long distances when frightened. Grasshoppers primarily feed on grasses & leaves. Their diet consists mostly of fresh plant material. Vital for their growth.
Many grasshopper species inhabit open fields. Meadows, & shrubs. These areas provide necessary resources for survival. Grasshoppers also exhibit diurnal behavior. Being most active during sunny days. Their preference for sunlight comes from their need for warmth. Such adaptations enhance their feeding & mating prospects.
Grasshoppers serve important ecological functions. They influence plant growth patterns through herbivory. Additionally. These insects act as prey for many birds & mammals. Their presence in ecosystems reflects broader biodiversity dynamics.
Physical Differences
Crickets & grasshoppers exhibit notable physical distinctions. Size may vary. But crickets tend To be larger overall. Crickets possess longer antennae compared with grasshoppers. Body shape also differs; crickets have cylindrical bodies. While grasshoppers appear flatter.
Coloration plays a role in identification. Crickets often display muted colors like brown or black. Grasshoppers may show more vibrant green shades. Aiding camouflage among vegetation. This difference helps each species blend effectively within its habitat.
Wings vary significantly between these insects. Crickets have longer. Softer wings that contribute To sound production. Grasshoppers have sturdier. Shorter wings meant for proficient jumping. These adaptations cater To their unique lifestyles & ecological roles.
Behavioral Similarities
Despite physical differences. Crickets & grasshoppers share behavioral similarities. Both insects exhibit communication through sound. Crickets produce musical calls. While grasshoppers produce simpler. Rhythmic sounds. Both strategies play roles in attracting mates & deterring rivals.
Another shared behavior involves mating rituals. During specific seasons. Males perform for females. They utilize sound or visual displays during courtship. These actions increase chances of successful reproduction for both species.
Both crickets & grasshoppers exhibit territorial behaviors. Males often defend their chosen areas from competitors. This behavior ensures access To resources & mating opportunities. Such territoriality supports reproductive success & population stability.
Dietary Preferences
Dietary choices further differentiate these two insects. Crickets are primarily detritivores. Consuming decaying organic matter. This characteristic aids in nutrient recycling within ecosystems. Grasshoppers primarily feed on fresh leaves & grasses. Showcasing more selective feeding habits.
Both insects play roles within their respective niches. By consuming plant matter. Grasshoppers influence vegetation structure. In contrast. Crickets support decomposition through their feeding habits. This ecological balance promotes diverse plant & animal interactions.
Diet affects habitat selection. Crickets thrive in environments abundant in organic material. Grasshoppers prefer areas with ample sunlight & fresh plant growth. Each insect’s unique adaptations reflect its specific nutritional needs & ecological preferences.
Vocalizations
Vocalizations represent one major distinction between crickets & grasshoppers. Crickets are known for their harmonic singing. This melody aids males in attracting potential mates. The sounds result from rapid wing movements. Creating intricate patterns.
In contrast. Grasshoppers produce distinctive rhythmic sounds. These noises result from wing rubbing. Though less complex than crickets. Grasshopper sounds also function as mating calls. Albeit less melodically. Both vocalizations serve similar purposes in reproduction.
Sound production illustrates adaptation To environments. Crickets’ songs thrive in ambient noise. Concealing their presence. Grasshoppers. Being diurnal. Benefit from daytime sounds. Each adaptation showcases how vocalizations support survival & reproductive strategies.
Habitat Preferences
Crickets & grasshoppers exhibit distinct habitat preferences. Crickets thrive in dark. Moist areas. Favoring leaf litter & undergrowth. Such environments offer protection from predators. Many species can adapt To urban settings where vegetation remains abundant.
Conversely. Grasshoppers prefer open. Sunny environments. Fields. Meadows, & gardens provide ideal habitats. These areas supply abundant food resources & ample sunlight. Grasshoppers often travel long distances within these spaces.
These habitat choices impact population dynamics. Crickets’ presence indicates healthy ground ecosystems. Grasshoppers offer insight into grassland health & management. Understanding these insects’ habitats allows for better conservation efforts.
Life Cycle & Reproduction
The life cycle for crickets consists of three stages: egg. Nymph, & adult. Females lay eggs in moist soil or plant material. Upon hatching. Nymphs resemble small adults but lack wings. Over time. Nymphs grow & undergo molting. Developing wings as they mature.
Grasshopper life cycles share similarities. Also comprising egg. Nymph, & adult stages. Females usually lay eggs in pods within soil. After hatching. Nymphs resemble miniature adult grasshoppers. Gradually developing fullsize wings & colors.
Reproductive strategies differ slightly between these insects. Crickets engage in more elaborate courtship displays. Grasshoppers rely primarily on simpler calls & visual signals. These methods contribute To each species’ evolutionary success.
| Feature | Cricket 🦗 | Grasshopper 🦗 |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | Detritivore | Herbivore |
| Habitat | Moist & Dark | Sunny & Open |
| Sound | Melodic | Rhythmic |
| Body Shape | Cylindrical | Flattened |
| Antennae Length | Long | Short |
Interactions Within Ecosystems
Both crickets & grasshoppers play vital roles in ecosystem dynamics. Predators vary but include birds. Amphibians, & mammals. These insects provide essential food resources for many wildlife species. Thus. They contribute significantly To biodiversity.
Moreover. Both insects influence vegetation through feeding activities. Grasshoppers’ herbivorous habits can control plant growth. Crickets aid decomposition. Enriching soil nutrient levels. This interaction strengthens overall ecosystem health & function.
Understanding their ecological interactions aids conservation efforts. As habitats change. These insects may face challenges. Preserving their populations helps maintain ecosystem balance & diversity. Conservation efforts should consider relationships within local environments.
Personal Experience
During childhood. I observed crickets & grasshoppers in my backyard. They fascinated me with their distinct behaviors & vibrant colors. Watching them provided endless entertainment & sparked my interest in nature.
I remember listening closely To cricket songs at night. Each sound brought a sense of calmness & inspiration. Grasshoppers jumped away whenever I approached. Showcasing their agility. Such moments ignited a lifelong passion for understanding insects.
This experience shaped my appreciation for nature’s nuances. Nature’s beauty unfolds in The smallest details. Observing these small creatures taught me valuable lessons about life & ecosystems.
Summary of Key Differences
Understanding The differences between crickets & grasshoppers aids appreciation for biodiversity. Various physical traits. Dietary needs, & audio communications define each insect. Through this knowledge. Enthusiasts can enhance their observations in nature.
Exploring similarities showcases shared adaptations aimed at thriving within ecosystems. Their mutual dependence on similar environmental conditions offers insights for studying ecosystems. This understanding fosters respect for both species & their habitats.
For more information. Visit RSPB Nature’s Home Magazine. Additionally. Explore details on Grasshoppers vs Crickets. Their behaviors & roles emphasize importance within ecological systems.
Learn more about various sports & their impact at History All Sports.
What are The main differences between crickets & grasshoppers?
Crickets typically have long. Slender bodies & long antennae. While grasshoppers are more robust with shorter antennae. Additionally. Crickets tend To be more nocturnal. Whereas grasshoppers are often active during The day.
Do crickets & grasshoppers produce sound differently?
Yes. Crickets produce a characteristic chirping sound by rubbing their wings together. A behavior known as stridulation. Grasshoppers. On The other hand. Produce sound by rubbing their hind legs against their wings.
What do crickets & grasshoppers eat?
Both insects are herbivorous. Primarily feeding on grasses & leaves. However. Crickets can also consume decaying plant material & fungi. While grasshoppers are more likely To eat fresh vegetation.
Are crickets & grasshoppers found in The same habitats?
Crickets & grasshoppers can inhabit similar environments. Such as grasslands & fields. However. Crickets are more often found in moist areas. Whereas grasshoppers thrive in drier. Sunnier locations.
How do The life cycles of crickets & grasshoppers differ?
Both insects undergo incomplete metamorphosis. But their life cycles can vary in duration. Crickets typically have a longer life cycle. Lasting several months. While grasshoppers develop faster. Often maturing within a few weeks.
Do crickets & grasshoppers have similar reproductive behaviors?
Yes. Both insects engage in similar reproductive behaviors. Such as males calling To attract females. However. The specifics of their mating calls & courtship rituals can differ significantly.
Are there any physical similarities between crickets & grasshoppers?
Both insects share similar body structures. Including long hind legs adapted for jumping & a segmented body. Their coloration can also be similar. Often blending with their surroundings for camouflage.
How do crickets & grasshoppers contribute To their ecosystems?
Both play vital roles as herbivores in ecosystems. Helping To control plant growth & serving as a food source for various predators. They also contribute To soil health through their feeding habits.
Can crickets & grasshoppers be found in urban areas?
Yes. Both insects can adapt To urban environments. Crickets may be found in gardens & backyards. While grasshoppers can thrive in parks & open green spaces.
What are The common predators of crickets & grasshoppers?
Both insects face similar predation threats from birds. Mammals, & other insects. Their ability To camouflage helps them avoid some predators. But they can still fall victim in their habitats.
Do crickets & grasshoppers have any economic significance?
Yes. Crickets are often used as bait in fishing & are also bred for animal feed. While grasshoppers are consumed in some cultures as a source of protein. Both insects can affect agriculture by impacting crop health.
Are crickets & grasshoppers subject To similar environmental stresses?
Yes. Both insects are affected by environmental factors such as habitat loss. Climate change, & pesticide use. These factors can impact their populations & distribution.
How do crickets & grasshoppers communicate with each other?
Crickets primarily communicate through sound. Using their chirping To attract mates & establish territory. Grasshoppers also communicate through sound but rely more on visual signals & body language.
Are crickets & grasshoppers considered pests?
Both insects can be viewed as pests when they damage crops or gardens. Their populations can sometimes explode. Leading To significant agricultural challenges.
Can crickets & grasshoppers coexist in The same environment?
Yes. Crickets & grasshoppers can coexist in The same environments. They often occupy different niches & have varying feeding habits. Which allows them To thrive alongside each other.
Conclusion
In conclusion, crickets & grasshoppers may look alike, but they have some key differences & similarities. They both belong To The same family of insects & share features like long legs for jumping. However, crickets are known for their musical chirps, while grasshoppers are usually quieter. Crickets prefer damp environments, whereas grasshoppers thrive in dry areas. Both play essential roles in their ecosystems, acting as food for various animals. Understanding these delightful insects helps us appreciate nature’s diversity. So next time you hear a cricket or see a grasshopper, you can recognize & enjoy their unique traits!











