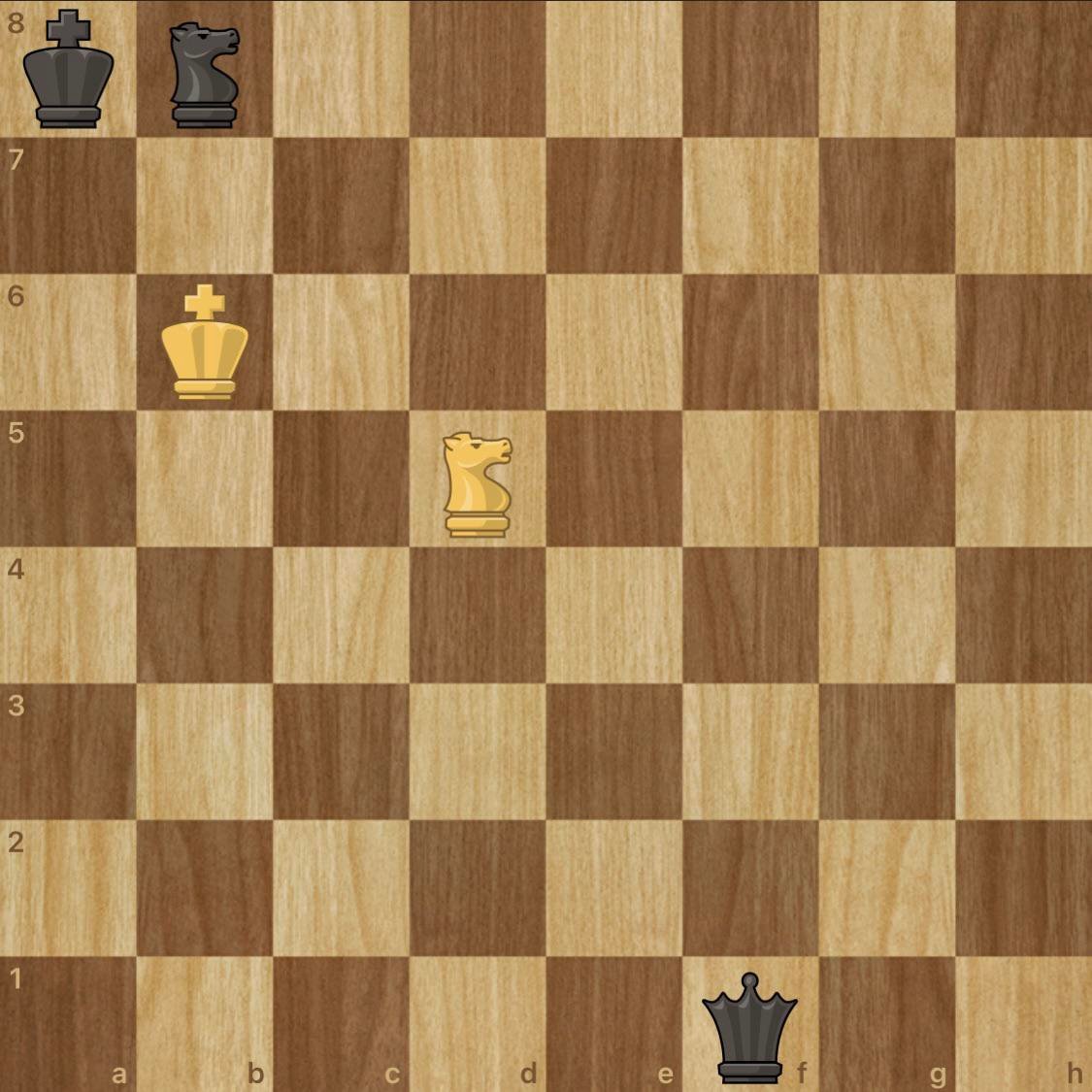
Stalemate in chess occurs when a player has no legal moves left but is not in check. This situation typically arises when one player has limited pieces or is in a cornered position, & any move would expose The king To check. It results in a draw. Symbolizing a situation where neither player can achieve victory despite one potentially having a material advantage. Stalemates often arise from tactical miscalculations. Forced play. Or deliberate strategies To escape a losing position. Adding an intriguing layer To The game’s complexities.
Stalemate in Chess: What It Is and How It Happens. Discover what a stalemate in chess is & how it happens. Learn The key signs & tips To avoid this tricky situation in your chess games. Let’s play smarter!
Stalemate in Chess: What It Is and How It Happens
Understanding Stalemate
Stalemate represents a unique situation in chess characterized by an inability for either player to make a legal move while one player does not face checkmate. This situation can arise in various forms. Confusing many. Including novice players. Awareness of how this gameending scenario functions allows players effective strategizing in achieving desired results.
Chess pieces occupy squares on a board. With the sole objective being checkmating opponent’s king. No possible moves available for one player while other player maintains king’s safety triggers a stalemate. Understanding chess mechanics becomes essential in recognizing when this scenario manifests during gameplay.
In my experience. Encountering a stalemate proved both frustrating and enlightening. I remember a specific match where becoming too aggressive left me vulnerable. Resulting in a surprising stalemate. This moment taught me valuable lessons regarding not only moves but also potential game outcomes.
How Stalemate Occurs
A stalemate can occur due to numerous factors. Often depending on positions of both players. Players must navigate through complexities of piece positioning while remaining aware that no legal moves available can trigger a stalemate. In most cases. One player dominates while forcing opponent into a position where no moves exist.
Players often overlook positions leading to stalemate. Specifically towards endgame when fewer pieces remain. In checkmate scenarios. Awareness helps. However. When a player doesn’t actively pursue checkmate. Allowing draw situations may happen unintentionally. Leading to confusion regarding game outcome. A thorough understanding helps prevent such instances.
Analyzing potential board positions. Players can spot patterns likely leading to stalemates. By recognizing scenarios where opponents could restrict movement without checkmating any pieces. Noticed trends can alter a player’s strategy for better outcomes in chess. For more insights. Visit this resource.
Common Situations Leading to Stalemate
Various situations can lead to stalemate during chess gameplay. Endgame scenarios frequently present opportunities allowing stalemates. Particularly when one side possesses limited pieces. Carefully observing position of pieces while minimizing movements can limit potential threats posed by an opponent.
Pieces with low mobility often contribute significantly towards stalemate scenarios. If a player finds themselves with only a king remaining. They must be cautious. Arranging their pieces such that they cannot face checkmate while allowing no other moves presents a pathway towards achieving stalemate.
Analyzing opponent’s strategies often encourages more defensive play styles. Reducing risk of falling into stalemate traps. Watching for strategies that utilize feigned weaknesses can keep a player from being lured into predictable traps. Effective management of position becomes crucial for both players involved.
Characteristics of Stalemate
- Ends game without winner 🥳
- Causes draw. Unable for player to move 🚫
- King not in check. But player has no legal moves 💡
- Can occur unexpectedly during endgame 🔍
- Requires strategic awareness for both players 📈
Stalemate vs Checkmate
Understanding differences between stalemate and checkmate crucial in chess. While stalemate results in a draw without clear winner. Checkmate signifies definitive victory for one player. Each situation possesses unique characteristics. Training oneself recognizes these nuances enhances gameplay.
In a checkmate scenario. King remains in check with no legal moves available. Leading directly towards loss for that player. Stalemate presents a distinct contrast. Allowing both players retain hope for improvement in future matches. As endpoints differ significantly.
Awareness of both conditions during matches influences strategy development. Players must navigate ongoing challenges. Maintaining flexible mindsets while focusing primarily on outcomes. Carefully monitoring each move allows prevention of both situations. Increasing chances for success on board.
Strategies to Avoid Stalemate
Implementing effective strategies helps avoid stalemate situations. Especially in crucial endgame scenarios. One fundamental principle includes maintaining an aggressive stance while pursuing advantageous positions throughout gameplay. Always aiming for checkmate ensures opponent feels pressured and encourages their reactive play style.
Additionally. Focusing on effective piece coordination assists in mitigating risk of stalemate. By ensuring pieces work together. While controlling key squares on board. Minimizes chances that opponent can maneuver into unforeseen stalemate scenarios. Thereby maximizing potential for victory.
Being aware of potential stalemate traps continually shifts focus during matches. Rethinking strategies. Remaining flexible. Allows for adaptation based on evolving board states. Continual learning through practice sessions and matches further develops a player’s understanding of avoiding stalemates during intense gameplay.
RealLife Examples of Stalemate in Competitive Matches
Stalemate scenarios frequently occur during competitive chess matches. Notable games highlight moments where players. Despite appearing to dominate. Ultimately faced unexpected stalemates. Observing these occurrences provides valuable insights into various styles employed by renowned players across chess history.
Consider historical matches where players displayed exceptional prowess yet made errors resulting in stalemate outcomes. Moments of excitement often followed these tense situations. Players’ reactions can be studied to analyze how different techniques influence overall strategies during critical gameplay phases.
Reflecting on personal experience during a recent tournament reminded me of how competitive atmospheres heighten tension around significant moves. Recognizing vital moments where stalemate could occur aids players in crafting effective responses aimed at maximizing success while minimizing chances falling into unanticipated traps.
Stalemate in Different Formats of Chess
Stalemate occurrences vary across chess formats. Influencing gameplay dynamics. With classical chess. Variants often present additional complexity regarding how players approach matches. Studying various rulesets allows expansion of strategies while ensuring topnotch performance throughout diverse match formats.
Rapid and blitz chess formats particularly amplify urgency. Introducing higher potential for stalemate situations due to time constraints. Players must make quick decisions. Which may lead them into precarious positions lacking viable escape routes. Ultimately resulting in unforeseen stalemates.
Online chess platforms also contribute towards different stalemate experiences. Various time controls and rule variations affect gameplay. Ensuring players adapt their strategies based on respective settings and dynamics associated with each format. Understanding specific characteristics contributes significantly towards players’ overall chess knowledge.
Famous Stalemate Games in History
Chess history showcases numerous famous games that ultimately resulted in stalemates. Notable matches reveal chess masters facing unexpected scenarios. Leading audiences to reflect on strategies resulting in these memorable outcomes. Gathering insights from historic matches enriches understanding regarding inherent complexities associated with chess gameplay.
Players can learn from studying positions frequently leading towards stalemate decisions. Analyzing moves made by renowned chess masters provides invaluable wisdom while fostering a deeper connection with chess history. Understanding how great players navigated through challenging situations proves beneficial for modern players honing their skills.
Resources documenting famous stalemate games remind players of importance regarding maintaining adaptability throughout matches. Analyzing past scenarios strengthens overall gameplay focus. Ensuring fewer mistakes occur during competitive encounters while augmenting strategic depth in upcoming matches.
Comparison of Stalemate and Draw Scenarios
| Aspect | Stalemate 🤝 | Other Draws 🌐 |
|---|---|---|
| Result | No winner. Game ends | No definitive outcome |
| Conditions | No legal moves available | Repeated moves. Insufficient material |
| Player’s Perspective | Defensive outcome | Neutral conclusion |
| Game Dynamics | Individual player choice | Mutual agreement. Rules violations |
Learning Resources for Stalemate Strategies
Exploring resources enhancing one’s understanding of stalemate scenarios proves beneficial for both beginners and experienced players. Many platforms offer tutorials. Articles. And videos detailing optimal strategies while emphasizing importance of maintaining awareness during game progression. Familiarity with quality resources enables players a greater appreciation regarding intricacies surrounding stalemate situations.
Numerous books delve into advanced strategies focusing on stalemate recognition and prevention. As players read through various analyses. They become equipped with knowledge needed towards improving their gameplay significantly. Engaging with friendly discussions and studying tutorial content broadens perspective regarding effective chess tactics.
Online chess communities also serve as valuable avenues for sharing experiences and discussing stalemate scenarios. Participating in forums creates opportunities for gaining insights while connecting with fellow enthusiasts. Ultimately discovering diverse perspectives on chess gameplay. For further exploration. Visit this link.
Discover what a stalemate in chess is & how it happens. Learn The key signs & tips To avoid this tricky situation in your chess games. Let’s play smarter!
| Specification | Stalemate in Chess | Draw in Chess | Checkmate in Chess | Resignation in Chess |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | A position where the player to move has no legal moves and their king is not in check. | A position that leads to a tie game without a winner. | A position where the opponent’s king is in check and there are no legal moves to escape. | A decision by a player to concede the game to their opponent. |
| Outcome | Result is a draw. | Result is a draw. | Result is a win for the opponent. | Result is a win for the opponent. |
| Involves King | Yes, the king cannot move legally. | Yes, the king is not in check. | Yes, king is checked. | Not directly related to king’s position. |
| Player’s Move | The player has no legal moves. | The player has no available winning moves. | The player has to respond to the check. | The player voluntarily chooses to end the game. |
| King’s Status | Not in check. | Not in check. | In check. | Not defined. |
| Material Advantage | Can occur regardless of material advantage. | Material difference can be present but does not influence the result. | Material often defines winning or losing. | Material may influence resignation. |
| Legal Moves | None possible for the player in turn. | Moves may still exist but lead to a drop in position. | Must consider check before moving. | Presence of moves may not matter. |
| Common Scenarios | Insufficient material on board, over-protecting the king. | Can result from stalemate or time control expiration. | Typically involves extensive development and tactical threats. | Usually occurs when a player feels a loss is imminent. |
| Player’s Choice | No choice when stalemate is reached; it’s automatic. | Players have the option to agree to a draw. | Player must react to being in check. | Player chooses to end the game. |
| Professional vs. Casual Play | Relevant in both; recognition can be strategic. | Common in tournament play, often a feature of advanced strategy. | Crucial in competitive settings, often well-studied. | Can be triggered by emotional or strategic responses. |
| Psychological Impact | Can lead to frustration if unexpected. | Both players may feel unsatisfied. | Can invoke stress and urgency. | May lead to regret or relief. |
| Enforcement in Tournaments | Rules apply equally; stalemate leads to a draw. | Draw agreements are regulated in rules. | Checkmate instances are also regulated. | Resignation recognized as valid reasoning for game end. |
| Understanding the Endgame | Stalemate often arises from endgame miscalculations. | Understanding potential draws in endgame is crucial. | Checkmate strategies require knowledge of endgame principles. | Player’s decision may reflect understanding of endgame dynamics. |
| Game Mechanics | Stalemate is a necessary part of the game rules. | Draws are a defined outcome in rules. | Checkmate ends the game as per rules. | Resignation is a mechanic within game ethics. |
| Educational Importance | Stalemate teaches valuable lessons about positioning. | Draw outcomes stress strategy over blind aggression. | Checkmate reinforces tactics and opponent pressure. | Resignation displays the importance of strategic foresight. |
| Historical Context | Stalemate scenarios noted in classic chess literature. | Studies on drawn positions have historical significance. | Checkmate techniques evolving over centuries. | Resignation practices have shifted with the game’s development. |
| Variations | Stalemate is consistent across chess variants. | Draw rules may vary by variant (e.g., no draws in bullet chess). | Checkmate principles remain the same generally. | Resignation is a common feature but may differ in impact based on variant. |
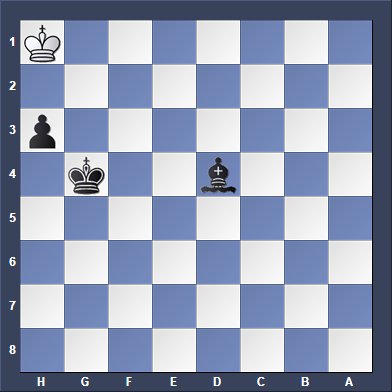
What is a stalemate in chess?
A stalemate occurs when a player has no legal moves left To make. Yet their king is not in check. This results in a draw. Meaning neither player wins The game.
How does a stalemate happen?
A stalemate can happen in various situations. Typically when one player has limited pieces left & The opponent has The opportunity To trap The king without delivering check.
Can a stalemate be intentional?
Yes. A player may intentionally create a stalemate To avoid losing a game when they are at a material disadvantage or in a losing position.
Does stalemate always end The game?
Yes. A stalemate results in an immediate end To The game, & The final result is a draw regardless of The positions of The other pieces on The board.
What are some common scenarios that lead To stalemate?
Common scenarios leading To stalemate include situations with few pieces left. Especially when a stronger player does not checkmate their opponent quickly enough & allows them To escape into stalemate.
Are there strategies To avoid stalemate?
Players can avoid stalemate by ensuring they always give their opponent legal moves & not rushing To checkmate when they have a material advantage.
Is stalemate a common outcome in chess games?
While stalemate is not The most common outcome. It does occur in both amateur & professional games. Especially as The number of pieces on The board decreases.
How is a stalemate different from a checkmate?
Stalemate is when The player cannot make a legal move but is not in check. While checkmate means The player’s king is in check & there are no available moves To escape The check. Resulting in a loss.
Can a stalemate be avoided by resigning?
Yes. A player can resign before a stalemate occurs. Effectively ending The game & conceding defeat. Rather than allowing it To reach a draw through stalemate.
What should a player do if they are close To reaching a stalemate?
If a player is close To reaching a stalemate. They should look for ways To create escape routes for their king or make moves that avoid trapping their king.
Conclusion
Stalemate in chess can be a tricky situation that sometimes catches players off guard. It occurs when one player has no legal moves left. But isn’t in check. Resulting in a draw. Understanding how stalemate happens is crucial for both beginners & seasoned players. It can shift The result of a game. Turning a potential win into a tie. Remember. Staying aware of your opponent’s possibilities is key To avoiding this outcome. So next time you play. Keep an eye out for those tricky positions To ensure you don’t fall into a stalemate & can push for victory instead!