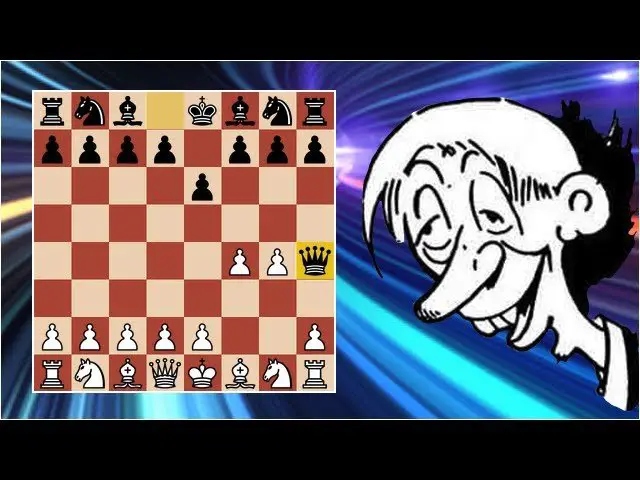
Fool’s Mate is The fastest way To win a chess game. Occurring in just two moves by leveraging your opponent’s mistakes. It unfolds when Black plays e2e4, & then White responds with f3 or g4. Exposing their king’s diagonal. If Black then moves Qh4. It delivers checkmate. As The White king has no escape squares, & The e3 pawn blocks The king from moving. Resulting in an instant victory. This specific scenario requires White To play uncharacteristically poorly. Making it a rare but illustrative example of how quickly a game can end with basic mistakes.
How to Win Chess in 4 Moves: Fool’s Mate Explained. Learn how To surprise your opponent with Fool’s Mate! Discover The quick 4move strategy To win chess easily & impress your friends. Let’s play smart!
How to Win Chess in 4 Moves: Fool’s Mate Explained
The Basics of Chess
Chess serves as a strategic game involving two players. Each player commands 16 pieces with unique movement capabilities. Understanding how each piece operates forms foundation for gameplay. Pawns. Rooks. Knights. Bishops. Queens. And kings present various tactics. Basic principles. Such as controlling center squares and developing pieces. Enhance chances of victory.
Envisioning positions on chessboard requires mental acuity. Players must anticipate several moves ahead while positioning pieces intelligently. Regular practice sharpens skills and leads to victories in competitive matches. Determination. Patience. And continuous learning serve as virtues for any chess player.
By incorporating tactical elements. Players foster analytical abilities beneficial in chess and other life scenarios. Many successful players analyze their games meticulously. Mistakes offer lessons. Ultimately leading towards improvement. Knowledge in chess grows with exploration and engagement.
What Fool’s Mate Entails
Fool’s Mate represents quickest way someone can achieve checkmate in chess. This scenario involves exploiting opponent’s poor opening strategy. It typically occurs when player proceeds without considering implications of moves. Within just four moves. Checkmate occurs. Culminating from fundamental mistakes.
Understanding Fool’s Mate becomes crucial for beginners. Familiarity with this concept not only helps recognize pitfalls but also strengthens overall play. Players who encounter Fool’s Mate often become wary of committing early blunders. Strategy and caution become paramount in early game stages. Compelling players to think critically.
Visualizing Fool’s Mate circumvents misunderstandings associated with basic gameplay. Players gain insight into how specific moves can lead opponents towards defeat. Absorbing various outcomes cultivates a deeper appreciation for chess. Engage frequently by practicing different scenarios to grasp mechanisms effectively.
Recognizing Patterns in Fool’s Mate
Chess often revolves around recognizing patterns. Fool’s Mate provides an opportunity for players to grasp basic tactical components. Key positions on board manifest best when attention focuses on potential threats. Players should train their eyes to spot potential opportunities for quick checkmates.
Engaging with books or online resources aids players in recognizing patterns such as Fool’s Mate. Resources investigating winning strategies frequently incorporate examples depicting various outcomes. Becoming familiar focuses efforts towards avoiding similar mistakes during matches.
Further. Dedicated practice cultivates instinctual understanding of board positions. Players develop habits that enable quick decisionmaking in critical moments. Training sessions emphasizing pattern recognition align with fundamental principles behind successful chess play.
Executing Fool’s Mate: A StepbyStep Guide
Execution of Fool’s Mate involves specific sequences. Commencing with white’s move. Typically involves advancing either pawn. Black must respond with an illadvised pawn move that opens diagonal pathway for queen or bishop.
Next. White may proceed by developing bishop or queen. Heading toward black’s king. Following this. Focusing on ensuring black’s king lacks adequate defenses leads towards subsequent moves. Often. Inexperienced players might overlook crucial threats. Which positions allow checkmate to materialize.
Upon establishing necessary conditions. Black’s king often finds itself in checkmate after four moves. Quick succession of errors leads towards inevitable defeat for black. Players mastering this strategy enhance their ability through quick thinking and decisionmaking prowess.
Critical Mistakes Leading to Fool’s Mate
Understanding typical errors leads players away from potential pitfalls. Poor openings remain common. Especially among newcomers. Allowing development of threatening pieces without deploying adequate defenses facilitates rapid demise.
Another misconception lies in believing strong pieces are sufficient. Neglecting proper pawn structure often results in weaknesses that experienced opponents can exploit. Awareness of mistakes potentially allows players to adjust their strategies moving forward.
Learning from prior blunders enables players to develop stronger game plans. Evaluating games creates teachable moments essential for growth. Players who dedicate time reflecting on their decisions tend to perform substantially better over time.
Features of Fool’s Mate
- ⚡ Rapid checkmate scenario
- 💡 Exploiting opponent’s mistakes
- 🔑 Teaches fundamentals of chess strategy
- 🎯 Ideal learning tool for beginners
- ⌛ Quick execution in just four moves
Personal Experience with Fool’s Mate
Reflecting on my journey through chess. Encountering Fool’s Mate opened my eyes towards strategic nuances that exist within this art. I remember initially struggling against this tactic. Which forced me to rethink my opening strategies. Learning from this experience ultimately fortified my skill set and allowed me to approach matches with a heightened sense of awareness.
Each encounter served as a learning opportunity. Analyzing my games helped me understand both basic moves and broader strategies necessary for success. As I practiced. I found myself increasingly adept at recognizing patterns. Leading toward a more comprehensive understanding of chess.
Over time. Engaging with varying strategies contributed significantly to growth. Dedication to practice allowed me to transform weaknesses into strengths while navigating complex game scenarios. Such experiences underline importance of continuous learning in chess.
Comparing Different Checkmate Strategies
| Strategy | Speed | Complexity | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fool’s Mate | ⚡ Fastest | 🔑 Very Simple | 💡 Beginners |
| Scholar’s Mate | 🏃♂️ Quick | 🔑 Beginner Friendly | 💡 New Players |
| Classic Checkmate | ⌛ Moderate | 🔑 Intermediate | 💡 Experienced Players |
Learning from Mistakes in Chess
All players encounter pitfalls at some stage during their chess journeys. Accepting mistakes. Particularly those leading towards unfortunate outcomes like Fool’s Mate. Becomes integral for growth. Analyzing each game’s course allows individuals to pinpoint tendencies needing retuning.
Engaging with fellow chess enthusiasts presents avenues for improvement. Sharing experiences fosters discussions revolving around strategic adjustments as well as identifying common errors. Such collaborations enable players to reflect internally while refining their understanding of chess.
Taking time reflects on each game helps avoid falling back into similar traps. Growth stems from being open towards feedback and understanding nuances contained in various strategies players employ. Committing oneself through practice ensures progression and discovery of enjoyable aspects inherent within chess.
For anyone interested in exploring more about sports. You can visit this guide.
Learn how To surprise your opponent with Fool’s Mate! Discover The quick 4move strategy To win chess easily & impress your friends. Let’s play smart!
| Feature | Description | Importance | Comparison Point | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Objective | To checkmate the opponent’s king in the fewest moves possible | High | Fastest checkmate strategy | Requires specific moves from the opponent |
| Sequence of Moves | 1. f3 e5 2. g4 Qh4# | Critical | Clear path to victory | Requires white to play inaccurately |
| Initial Position | Standard chess starting position | Essential | Universal starting point for all chess games | Applicable in any standard chess match |
| Opponent’s Response | Must play poorly for Fool’s Mate to occur | High | Predictability of moves | Showcases the necessity of understanding of basic openings |
| Strategy Type | Opening tactic | Important | Focus on early game advantage | Emphasizes aggressive play |
| Risk Level | Very high for white; low for black | Moderate | Risk versus reward analysis | Not recommended for serious play |
| Common Usage | Used primarily as a teaching tool | High | Understanding basic checkmates | Ideal for beginners |
| Counter Strategy | Be aware of the risks involved in pawn moves | Critical | Defense mechanisms | Important for player development |
| Complexity | Simple to execute | Low | Ease of learning | Accessible for all skill levels |
| Famous Practitioners | Not typically used by advanced players | Rare | Level of player utilization | Almost mythical in nature |
| Game Duration | Typically under a minute | High | Time efficiency | Quick resolution in gameplay |
| Learning Curve | Minimal for beginners | Low | Initial game understanding | Foundational strategy for new players |
| Theory Support | Widely recognized as a fundamental concept | High | Educational relevance | Often discussed in chess literature |
| Psychological Aspect | Exploits overconfidence of the opponent | Moderate | Mind games in chess | Can lead to mental weaknesses |
| Countering Fool’s Mate | Develop pieces correctly and avoid weakness | Critical | Importance of defense | Encourages strategic thinking |
| Post-Game Analysis | Reviewing the opponent’s mistakes | High | Learning from losses | Key for growth in chess skills |
| Variations | Not many other than standard openings | Low | Diversity of strategies | Focus on simplicity |
| Further Applications | Understanding aggressive strategies and openings | High | Broader chess strategy implications | Serves as a foundation for complex strategies |
| Effectiveness in Real Games | Rarely successful at higher levels | Low | Real-world application | More of a fun anecdote than a reliable strategy |
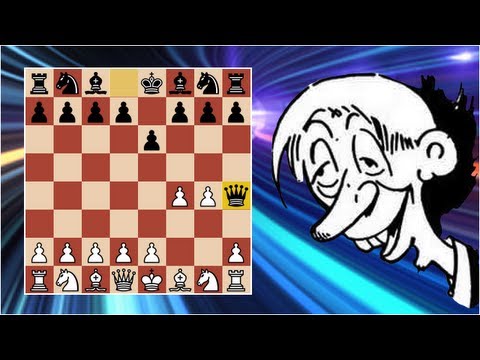
What is Fool’s Mate in chess?
Fool’s Mate is The name given To The fastest possible checkmate in chess. Occurring in just two moves. It exploits The weakness of an unprepared opponent. Specifically targeting The f7 square.
How does Fool’s Mate happen?
Fool’s Mate occurs when The player with The black pieces checkmates The white king on The second move of The game. It happens if White plays poorly. Moving The pawns in front of The king & queen. Allowing for an easy checkmate.
What moves lead To Fool’s Mate?
The typical moves leading To Fool’s Mate are 1. f3 & 2. g4 for White. Followed by 2…Qh4# for Black. In this scenario. Black’s queen delivers checkmate, & White has no pieces capable of blocking or capturing The queen.
Can an experienced player fall for Fool’s Mate?
An experienced player is very unlikely To fall for Fool’s Mate. As it requires two blatant mistakes from White. It’s more common among beginners who may not be aware of basic opening principles.
What are The key opening principles To avoid Fool’s Mate?
To avoid Fool’s Mate. Players should control The center of The board. Develop their pieces, & avoid moving The pawns in front of The king & queen too early in The game. Ensuring that these guidelines are followed can help prevent quick checkmates.
Why is it important To learn about Fool’s Mate?
Understanding Fool’s Mate & other traps helps players recognize potential threats & improve their overall strategy. It emphasizes The importance of solid opening moves & The dangers of exposing The king during early play.
Are there any variations of Fool’s Mate?
While The classic Fool’s Mate consists of specific moves. Variations may occur based on The specific moves of The opponent that still lead To a very quick checkmate. However. The basic idea remains The same: taking advantage of poor pawn structure around The king.
What psychological aspects are involved in Fool’s Mate?
Fool’s Mate can illustrate The importance of patience & strategic thinking. Impatience or overconfidence can lead To mistakes. Demonstrating how quickly a strong position can turn into a defeat.
How can beginners practice To avoid Fool’s Mate?
Beginners can practice by playing games & reflecting on their opening moves. Studying basic principles & practicing against opponents of varying skill levels can help reinforce The importance of sound beginning strategies.
Is there any significance To Fool’s Mate in chess culture?
Fool’s Mate has become a popular example in chess literature & education due To its simplicity & The lesson it imparts about The importance of defending The king. It serves as a memorable warning against poor opening strategies.
Conclusion
Winning in chess can be quick & surprising. Just like with Fool’s Mate. Remember. This strategy only works if your opponent makes a big mistake by opening up their king too much. While it’s fun To know this quick win. Focus on improving your overall game for lasting success. Practice different openings & strategies, & watch how your skills grow. Chess is all about thinking ahead & learning from each game. So. Whether you pull off a swift victory or not. Enjoy every moment on The board & keep playing! Happy chessing!